ฉันจะเรียกใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้ใน windows ได้อย่างไร:
$ sudo django-admin.py startproject NEW
เหรอ?
ฉันจะเรียกใช้คำสั่งต่อไปนี้ใน windows ได้อย่างไร:
$ sudo django-admin.py startproject NEW
เหรอ?
คำตอบ:
ไม่มีsudoคำสั่งใน Windows ค่าเทียบเท่าที่ใกล้ที่สุดคือ "run as administrator"
คุณสามารถทำได้โดยใช้runasคำสั่งกับระดับความน่าเชื่อถือของผู้ดูแลระบบหรือคลิกขวาที่โปรแกรมใน UI แล้วเลือก"run as administrator"
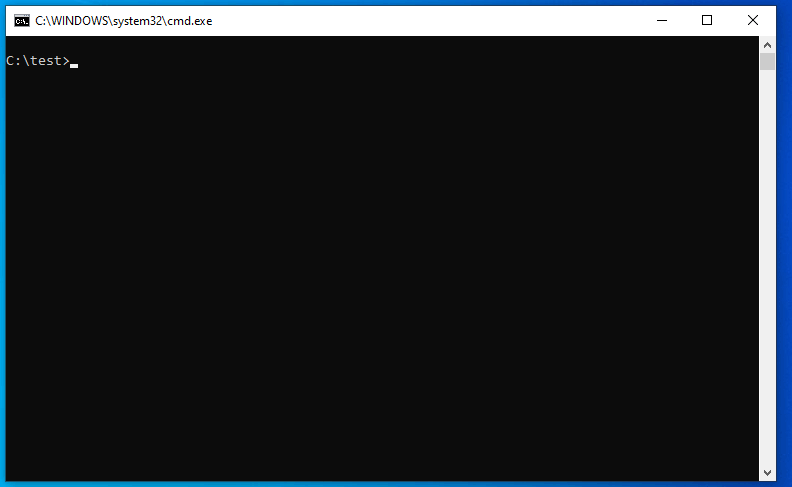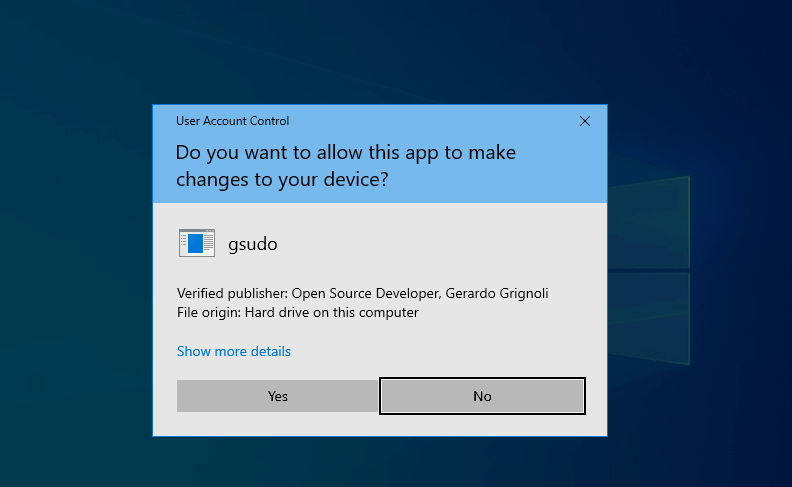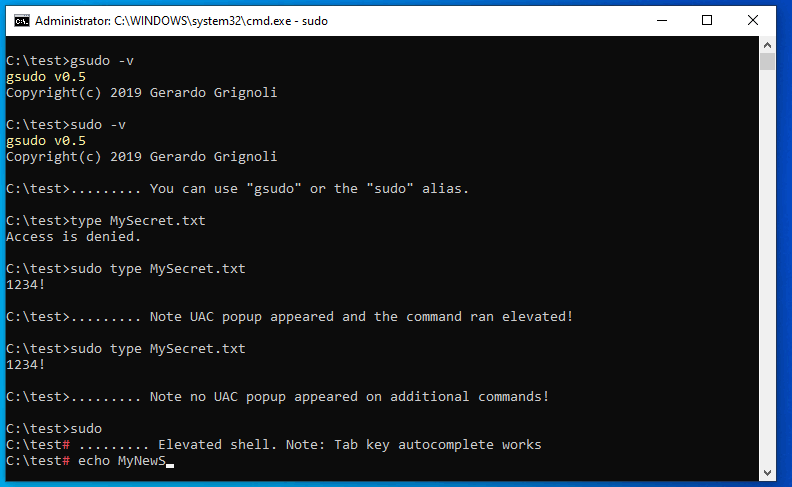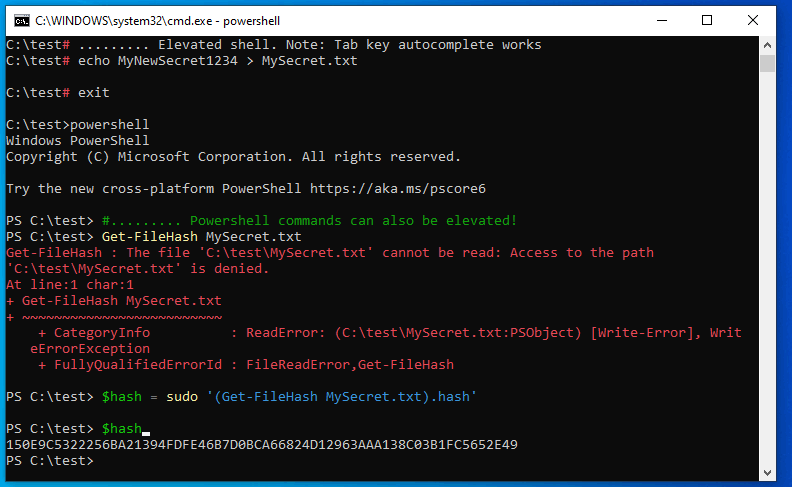
gsudo( stackoverflow.com/a/58753166/97471 ) เป็น sudo สำหรับ windows ที่มี*nix sudoประสบการณ์ผู้ใช้: อนุญาตให้ดำเนินการคำสั่งภายในคอนโซลปัจจุบันและแคชข้อมูลรับรอง (ป๊อปอัป UAC เพียงรายการเดียว)
เปิด notepad และวางรหัสนี้:
@echo off
powershell -Command "Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/c cd /d %CD% && %*'"
@echo on
Then, save the file as sudo.cmd. Copy this file and paste it at C:\Windows\System32 or add the path where sudo.cmd is to your PATH Environment Variable.
When you open command prompt, you can now run something like sudo start ..
If you want the admin command prompt window to stay open when you run the command, change the code in notepad to this:
@echo off
powershell -Command "Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/k cd /d %CD% && %*'"
@echo on
Explanation:
powershell -Command runs a powershell command.
Start-Process is a powershell command that starts a process, in this case, command prompt.
-Verb RunAs runs the command as admin.
-Argument-List runs the command with arguments.
Our arguments are '/c cd /d %CD% && %*'. %* means all arguments, so if you did sudo foo bar, it would run in command prompt foo bar because the parameters are foo and bar, and %* returns foo bar. cd /d %CD% is a command to go to the current directory. This will ensure that when you open the elevated window, the directory will be the same as the normal window. the && means that if the first command is successful, run the second command.
The /c is a cmd parameter for closing the window after the command is finished, and the /k is a cmd parameter for keeping the window open.
Credit to Adam Plocher for the staying in the current directory code.
C:\Windows\System32.
powershell -Command "Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/k cd /d %CD% && %*'"
echo lines one and three by prepending @ to the powershell line?
All the answers explain how to elevate your command in a new console host.
What amused me was that none of those tools behave like *nix sudo, allowing to execute the command inside the current console.
So, I wrote: gsudo
Source Code https://github.com/gerardog/gsudo
Via scoop
scoop install gsudo
Or via Chocolatey
choco install gsudo
Manual instalation:
I've created wsudo, an open-source sudo-like CLI tool for Windows to run programs or commands with elevated right, in the context of the current directory. It's available as a Chocolatey package.
I use it a lot for stuff like configuring build agents, admin things like sfc /scannow, dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth or simply for installing/updating my local Chocolatey packages. Use at your own risk.
choco install wsudo
Chocolatey must be already installed.
wsudo is a Linux sudo-like tool for Windows to invoke a program with elevated rights (as Administrator) from a non-admin shell command prompt and keeping its current directory.
This implementation doesn't depend on the legacy Windows Script Host (CScript). Instead, it uses a helper PowerShell 5.1 script that invokes "Start-Process -Wait -Verb runAs ..." cmdlet. Your system most likely already has PowerShell 5.x installed, otherwise you'll be offered to install it as a dependency.
wsudo runs a program or an inline command with elevated rights in the current directory. Examples:
wsudo .\myAdminScript.bat
wsudox "del C:\Windows\Temp\*.* && pause"
wasudo cup all -y
wasudox start notepad C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
For more details, visit the GitHub repro.
wasudo made it easier for you. I myself mostly live in the VSCode integrated console terminal, so I just type wasudo there :) The next improvement would be to inherit the environment vars.
runas command requires the users to type password.
If you don't want to type password and want to just click the UAC dialog, use Start-Process -Verb runas in PowerShell instead of runas command.
You normally wouldn't, since you wouldn't run it under *nix regardless. Do development in a user directory, and deploy afterwards to system directories.
in Windows, you can use the runas command. For linux users, there are some alternatives for sudo in windows, you can check this out
http://helpdeskgeek.com/free-tools-review/5-windows-alternatives-linux-sudo-command/
There kind of is. I created Sudo for Windows back in 2007? 08? Here's the security paper I wrote about it - https://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/bestprac/sudo-windows-sudowin-1726. Pretty sure http://sudowin.sf.net still works too.
You could use runas command - http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb490994.aspx or sudowin - http://sourceforge.net/projects/sudowin/
The following vbs script allows to launch a given command with arguments with elevation and mimics the behavior of the original unix sudo command for a limited set of used cases (it will not cache credentials nor it allows to truly execute commands with different credentials). I put it on C:\Windows\System32.
Set objArgs = WScript.Arguments
exe = objArgs(0)
args = ""
IF objArgs.Count >= 2 Then
args = args & objArgs(1)
End If
For it = 2 to objArgs.Count - 1
args = args & " " & objArgs(it)
Next
Set objShell = CreateObject( "WScript.Shell")
windir=objShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings("%WINDIR%")
Set objShellApp = CreateObject("Shell.Application")
objShellApp.ShellExecute exe, args, "", "runas", 1
set objShellApp = nothing
Example use on a command prompt sudo net start service
I think I tried steps below after doing some research & succeeded
1.Install scoop using powershell 3 (iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('https://get.scoop.sh')) 2. do scoop install --global sudo 3. make sure paths (C:\Users\\scoop\shims & C:\ProgramData\scoop\shims) added in environmental path variable.
There is no sudo command in case of windows and also there is no need to put any $. For installing Angular CLI through node.js command prompt in windows, I just wrote npm install -g @angular/cli and then pressed Enter. It worked fine.
open the console as a administrator. Right Click on the command prompt or bash -> more and select "run as administrator"
In Windows Powershell you can use Start-Process command with option -Verb RunAs to start and elevated process.
Here is my sudo function example:
function sudo {
Start-Process @args -verb runas
}
Ex: Open hosts file as Admin in notepad
sudo notepad C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
Using the sudo command for window users gives you the following suggestions:
First, install the scoop package management tool and execute the following commands:

Then use scoop to install the sudo command:

Finally, you can execute the command with sudo:

I am glad to help you.
To make a sudo command follow the steps :-
Hope this will help you
To just run a command as admin in a non-elevated Powershell, you can use Start-Process directly, with the right options, particularly -Verb runas.
It's a lot more convoluted than sudo, particularly because you can't just re-use the previous command with an additional option. You need to specify the arguments to your command separately.
Here is an example, using the route command to change the gateway :
This fails because we are not in an elevated PS:
> route change 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.3
The requested operation requires elevation.
This works after accepting the UAC:
> Start-Process route -ArgumentList "change 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.3" -Verb runas
Or for a command that requires cmd.exe:
> Start-Process cmd -ArgumentList "/c other_command arguments ..." -Verb runas