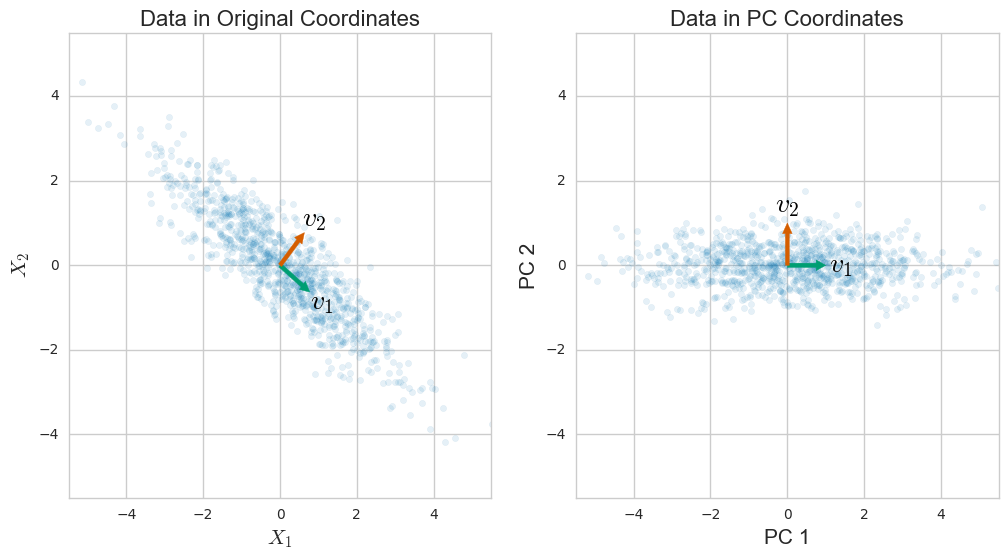
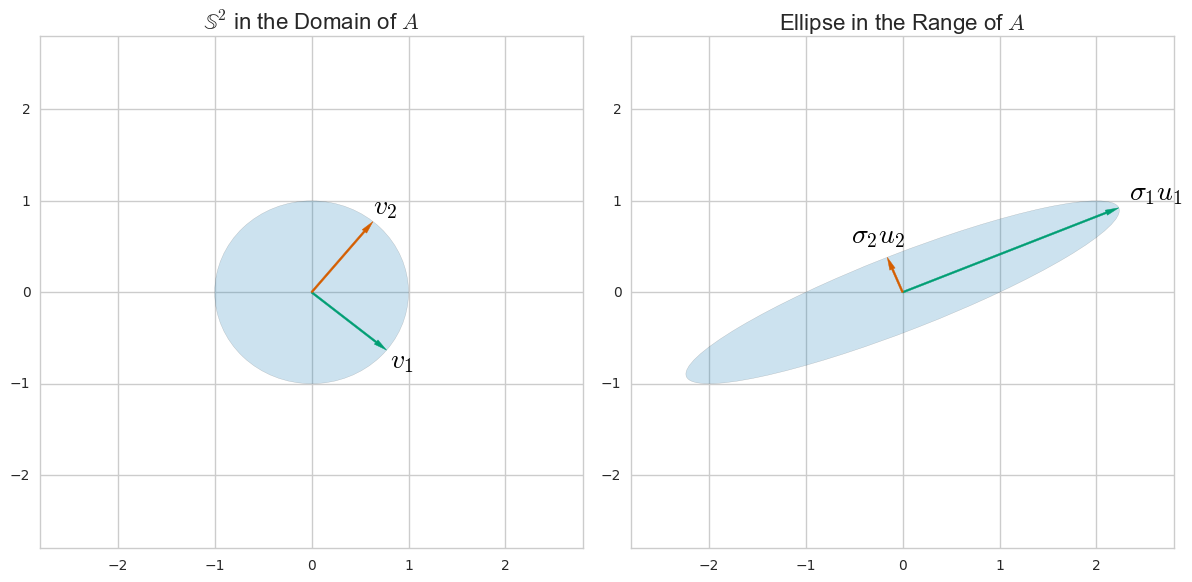
ฉันเขียน Python & Numpy snippet ที่มาพร้อมกับคำตอบของ @ amoeba และฉันจะทิ้งไว้ที่นี่ในกรณีที่มันมีประโยชน์สำหรับใครบางคน ความคิดเห็นส่วนใหญ่นำมาจากคำตอบของ @ amoeba
import numpy as np
from numpy import linalg as la
np.random.seed(42)
def flip_signs(A, B):
"""
utility function for resolving the sign ambiguity in SVD
http://stats.stackexchange.com/q/34396/115202
"""
signs = np.sign(A) * np.sign(B)
return A, B * signs
# Let the data matrix X be of n x p size,
# where n is the number of samples and p is the number of variables
n, p = 5, 3
X = np.random.rand(n, p)
# Let us assume that it is centered
X -= np.mean(X, axis=0)
# the p x p covariance matrix
C = np.cov(X, rowvar=False)
print "C = \n", C
# C is a symmetric matrix and so it can be diagonalized:
l, principal_axes = la.eig(C)
# sort results wrt. eigenvalues
idx = l.argsort()[::-1]
l, principal_axes = l[idx], principal_axes[:, idx]
# the eigenvalues in decreasing order
print "l = \n", l
# a matrix of eigenvectors (each column is an eigenvector)
print "V = \n", principal_axes
# projections of X on the principal axes are called principal components
principal_components = X.dot(principal_axes)
print "Y = \n", principal_components
# we now perform singular value decomposition of X
# "economy size" (or "thin") SVD
U, s, Vt = la.svd(X, full_matrices=False)
V = Vt.T
S = np.diag(s)
# 1) then columns of V are principal directions/axes.
assert np.allclose(*flip_signs(V, principal_axes))
# 2) columns of US are principal components
assert np.allclose(*flip_signs(U.dot(S), principal_components))
# 3) singular values are related to the eigenvalues of covariance matrix
assert np.allclose((s ** 2) / (n - 1), l)
# 8) dimensionality reduction
k = 2
PC_k = principal_components[:, 0:k]
US_k = U[:, 0:k].dot(S[0:k, 0:k])
assert np.allclose(*flip_signs(PC_k, US_k))
# 10) we used "economy size" (or "thin") SVD
assert U.shape == (n, p)
assert S.shape == (p, p)
assert V.shape == (p, p)